Tag: regression. Page 2
Structural equation model trees with partykit and lavaan
news
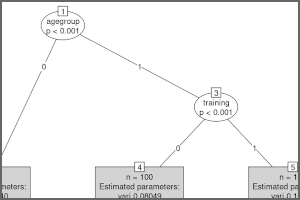
To capture heterogeneity in structural equation models (SEMs), the model-based recursive partitioning (MOB) algorithm from partykit can be coupled with SEM estimation from lavaan. Read more ›
lmSubsets: Exact variable-subset selection in linear regression
news
The R package lmSubsets for flexible and fast exact variable-subset selection is introduced and illustrated in a weather forecasting case study. Read more ›
Circular regression trees and forests
news
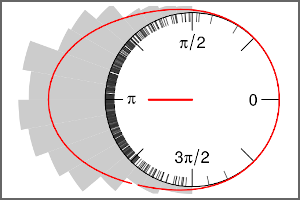
A flexible framework for probabilistic forecasting of circular data is introduced, using distributional regression trees and random forests based on the von Mises distribution. Read more ›
bamlss: A Lego toolbox for flexible Bayesian regression

news
Modular R tools for Bayesian regression are provided by bamlss: From classic MCMC-based GLMs and GAMs to distributional models using the lasso or gradient boosting. Read more ›
Network model trees
news
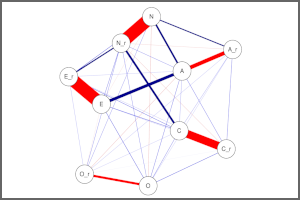
The effect of covariates on correlations in psychometric networks is assessed with either model-based recursive partitioning (MOB) or conditional inference trees (CTree). Read more ›
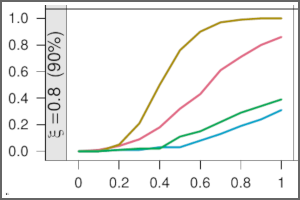
The power of unbiased recursive partitioning
news
The significance tests underlying the unbiased tree algorithms CTree, MOB, and GUIDE are embedded into a unifying framework. This allows to assess relative strengths and weaknesses in a variety of setups, highlighting the advantages of score-based tests (as in CTree/MOB) vs. residual-based tests (as in GUIDE). Read more ›
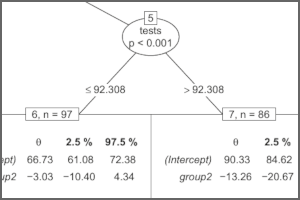
Personalized treatment effects with model4you
news
Personalized treatment effects can be estimated easily with model-based trees and model-based random forests using the R package model4you. Read more ›
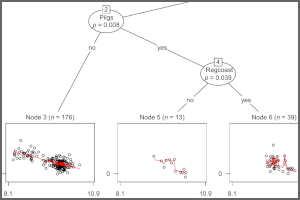
Spatial lag model trees
news
Economic growth models are recursively partitioned to assess heterogeneity in growth and convergence across EU regions while adjusting for spatial dependencies. Accompanied by R package lagsarlmtree, combining partykit::mob and spdep::lagsarlm. Read more ›
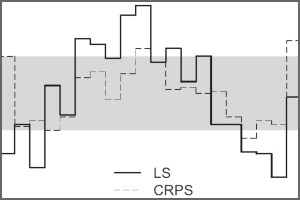
Minimum CRPS vs. maximum likelihood
news
In a new paper in Monthly Weather Review, minimum CRPS and maximum likelihood estimation are compared for fitting heteroscedastic (or nonhomogenous) regression models under different response distributions. Minimum CRPS is more robust to distributional misspecification while maximum likelihood is slightly more efficient under correct specification. An R implementation is available in the crch package. Read more ›
Partially additive (generalized) linear model trees
news
The PALM tree algorithm for partially additive (generalized) linear model trees is introduced along with the R package palmtree. One potential application is modeling of treatment-subgroup interactions while adjusting for global additive effects. Read more ›